Browse Exhibits (4 total)
Behold, The Amazing Bearded Woman!
Why are only women able to bear children? Why do men have nipples? How do you determine gender to someone androgynous? What is really going on inside of us? These are just some of the questions that plagued the minds of doctors, philosophers and artists alike. Seeking these answers demanded an invasive and taboo analysis of the human body inside and out.
The growing interest in gender and the human body in the 15th century created a grotesquely beautiful genre of treatises and art that used human corpses as its muse. Anatomy theaters were where students of medicine and men of science would gather to watch dissections take place. Artists were employed to sketch and develop woodcuts and engravings for treatises and other printed texts with images.[1] The fascination with the inner-working of humans had soon expanded from the circles of those in medicine to the artists. Artists like Albrecht Durer, Leonardo da Vinci, and Rembrandt saw man as the measure of all things. They displayed a mechanical eye for accuracy and a realistic portrayal of the human body. Artists in this period had begun to study fields normally allocated to intellects, philosophers, scientists, and doctors. The combination of the arts and sciences revolutionized the way humans shared knowledge of medicine and Anatomy.
Little was known about female anatomy largely because of the lack of female cadavers dissected in the early years of anatomical studies. Anatomists, doctors, and other men of science and medicine were fascinated with the females ability to give birth. [2] The more they learned about the anatomy of men and women, the more interesting cases of hermaphrodites and eunuchs became. Humans are comforted by having things put into categories, these cases of gender deformity and oddity were not so easily categorized. [3] Today gender is still a concept that is under analysis and scrutiny.
1. Paula Findlen, “Anatomy Theatres, Botanical Gardens, and Natural History Collections,” in The Cambridge History of Science, eds. Katharine Park and Lorraine Daston (Cambridge, MA: Cambridge University Press, 2016), 272-89
2. Monica Azzolini, “Exploring Generation: A Context to Leonardo’s Anatomies of the Female and Male Body,” in Leonardo da Vinci’s Anatomical World, ed. Domenico Laurenza and Alessandro Nova (Venezia: Marsilio, 2011), 79-97
3. Lilian H. Zirpolo, “Depicting Sexual Deformity in Early Modern Art: Scientific, Medical, and Socio-Cultural Considerations, Part I-Excess and Absence,” in Vanishing Boundaries: Scientific Knowledge and Art Production in the Early Modern Era, ed. A. Victor Coonin and Lilian H. Zirpolom (Ramsey, NJ: WAPACC Organization, 2015). 113-64
Optics in Art
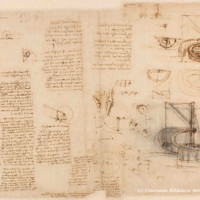
Optics: The scientific study of sight and the behavior of light, or the properties of transmission and deflection of other forms of radiation. (1)
There were many major developments made during the early modern period in Europe. One area of major development was in the field of optics. Scholars like Leonardo da Vinci and Matteo Zaccolini studied optics and made critical discoveries that laid the groundwork for generations of research and advancements to come. With these developments came the implementation of this newfound knowledge into art, specifically painting. Many painters used their knowledge of optics and made use of optic instruments to enhance their paintings and make them more realistic. This caused a shift in the style of painting toward naturalism. This exhibition focuses on two major treatises from the early modern period in Europe and the effect they had on the world of art.
Citations:
1. "Dictionary.com." Dictionary.com. Accessed May 1, 2018. http://www.dictionary.com/.